Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) – The Comprehensive Prescribing Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Content
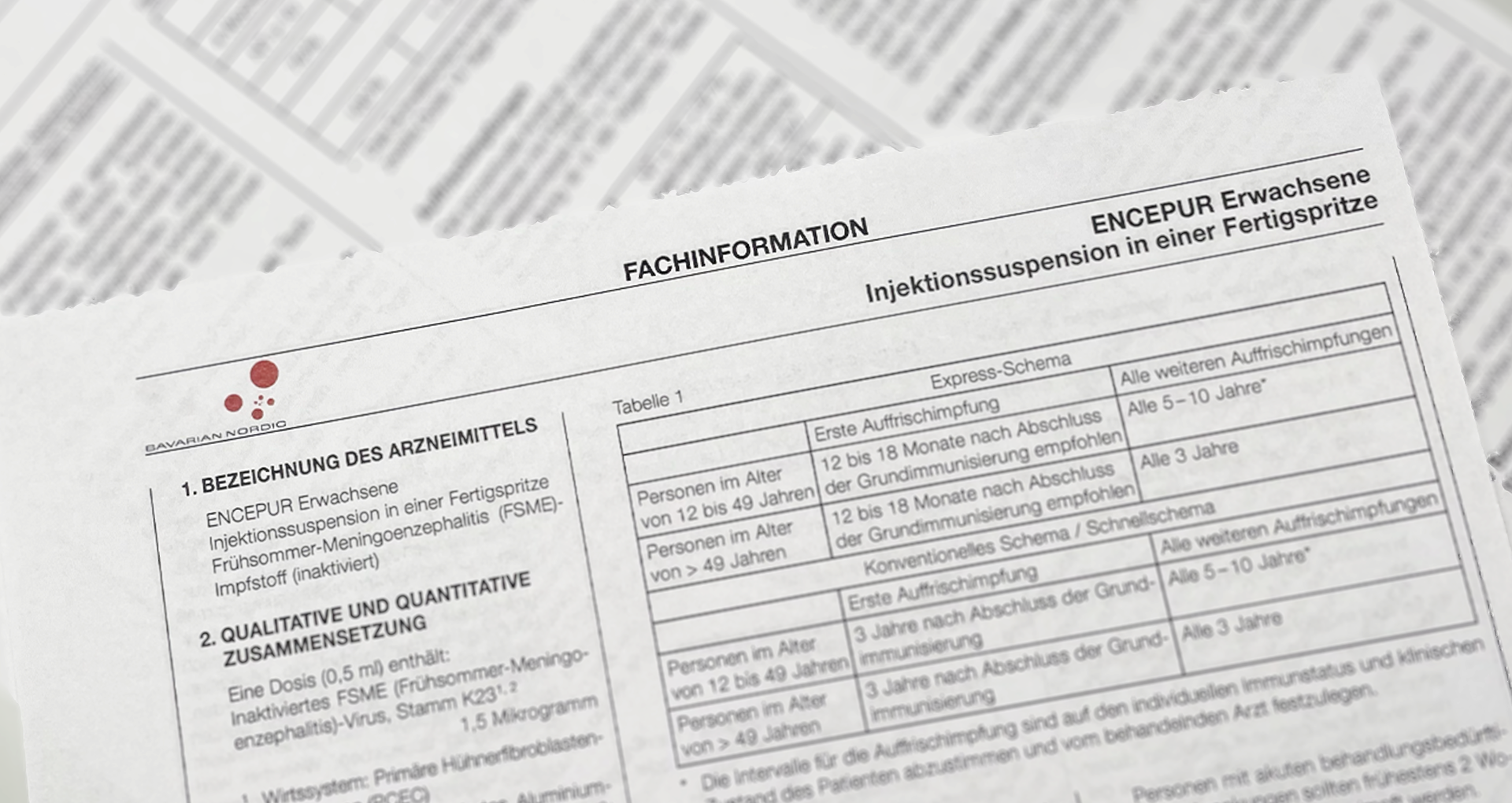
What is Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)?
Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) are legally prescribed, scientifically based documents that contain detailed information on a medicinal product. They serve as the primary source of information for healthcare professionals, in particular doctors, pharmacists and other healthcare professionals. The contents of the SmPC are determined in close consultation with the regulatory authorities and are essential for the correct application and safe use of a medicine.
Typically, the Summary of Product Characteristics contains:
- Active substance, pharmaceutical form and composition of the preparation
- Indications (areas of application) and contraindications
- Dosage and method of use
- Interactions with other medicines
- Side effects and risks
- Pharmacological and clinical properties
Since, unlike package leaflets, expert information is not intended for patients but for healthcare professionals, it must not contain any simplifications that are easily understood by laypersons. Instead, they are formulated with scientific precision and are based on the current study data that led to the approval of the medicine.
Legal basis and requirements
In Europe, summary of product characteristics is governed by various legal regulations, in particular the German Medical Products Act (AMG) and the requirements of the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In addition, national authorities such as the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) or the Paul Ehrlich Institute (PEI) play a central role in the approval and updating of these documents.
The most important legal requirements include:
- Correctness and completeness of the information
- Regular updating based on new scientific findings
- Clear and unambiguous language to avoid misinterpretation
- Mandatory provision for specialist circles, usually in digital or printed form
Particularly in the course of digitalization, specialist information is now increasingly available online, for example via portals such as Rote Liste®, Gelbe Liste® or Fachinfo-Service®. These make it easier for doctors and pharmacists to access up-to-date information and enable quick verification of drug data.
Summary of Product Characteristics vs. patient information
Although information for healthcare professionals and information for patients have the same origin – namely the officially approved data on the medicinal product – they differ significantly in their target group, language and level of detail.
Summary of Product Characteristics:
- Aimed at healthcare professionals
- Contains detailed scientific information
- Uses medical-pharmacological terminology
- Serves for well-founded decision-making for diagnoses and therapies
Instructions for use (package leaflet):
- Aimed directly at patients
- Contains explanations in layman’s terms
- Must pay attention to clear, simple formulations
- Largely dispenses with technical terms
In pharmaceutical practice, both types of document are closely linked, as doctors and pharmacists must not only understand the technical information, but also be able to communicate it in a patient-friendly way.
Integration of SPC in digital channels
With the digitalization of the healthcare sector, specialist information is undergoing a profound transformation. While it used to be available mainly in printed form or as PDF documents, it is now increasingly being integrated into digital systems, including:
- Electronic drug databases for doctors and pharmacists
- Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) that integrate FI data directly into diagnostic systems
- Mobile apps for physicians that provide quick access to up-to-date drug information
- Interactive platforms that provide real-time updates on side effects or newly approved indications
The importance of SPC for the pharmaceutical industry
Technical information often forms the basis for efficacy claims and frequently serves as a referenced source in marketing messages to medical professionals:
- Scientific basis of trust: specialist information serves as an objective basis for medical discussions with doctors and pharmacists.
- Content basis for training materials: They form the basis for further training, specialist medical articles or webinars.
- Increase digital reach: Pharmaceutical companies optimize their digital channels to provide doctors with structured specialist information in a targeted manner – for example via interactive websites, whitepapers or personalized specialist newsletters.
- Compliance with regulatory advertising guidelines: While direct advertising of prescription drugs to patients is prohibited, pharmaceutical companies are allowed to inform doctors via FI-based channels, e.g. through medical congresses or certified specialist portals.
Conclusion: SPC as the key to safe use of medicines
SPCs (Summary of Product Characteristics) represent an indispensable foundation for the safe and appropriate use of medicines. They are legally anchored, scientifically substantiated, and tailored specifically to the needs of healthcare professionals. Unlike the patient information leaflet, they are characterized by precision, completeness, and the use of specialized terminology.
With advancing digitalization, SPCs are gaining increasing importance, as they can be seamlessly integrated into electronic systems, thereby supporting rapid, evidence-based decision-making.
For the pharmaceutical industry, they serve not only as regulatory mandatory documents but also as a central basis for communication, training, and marketing within professional circles. Thus, SPCs combine scientific accuracy with practical applicability, forming an essential link between regulatory requirements, medical practice, and modern knowledge transfer.
